VBA programming for evaluation tools in the laboratory
ACOMED statistics works for clinical research laboratories in the pharmaceutical industry, from IvD manufacturers and laboratory medicine. In addition to statistical planning and analysis, there is sometimes a need for tools for single-user solutions with the ease of use of Excel, the statistical variety of R and the depth of validation of the FDA in the context of routine evaluations. ACOMED statistik offers individual software solutions in MS Excel (VBA programming, possibly with the integration of programs in R).
As the two examples show, the tools mostly arise in connection with development work with regard to the statistical methodology.
These Excel solutions are extensively validated depending on the requirements of the client (e.g. double programming, parallel programming in SAS, checking using examples, sometimes including unfavorable constellations, etc.).
It should be noted that these are time-consuming and costly projects. The specification was made together with the client. This interactive process requires flexibility on both sides, as is usually the case in long-term, good business relationships.
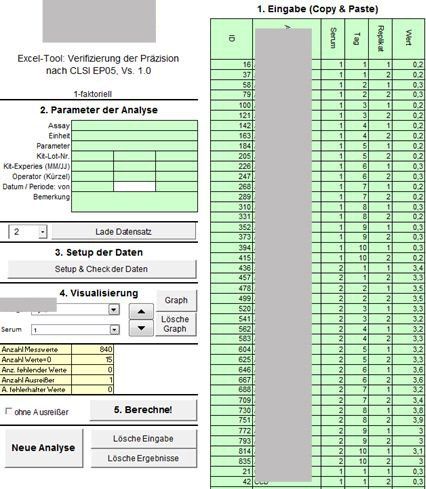
Example: Evaluation of precision experiment according to CLSI EP05 for multi-parameter assay for IvD manufacturers
Task:
For a multi-parameter assay with approx. 20 parameters, a precision experiment according to CLSI EP05 with the factors day and lot should be carried out on patient samples. From this experiment, the repeatability as well as the between-lot and between-day precision are to be determined for each parameter. There is only limited sample material available per patient. In addition, the concentration cannot be controlled for each measurement parameter.
Methodological solution:
The experiment is carried out on many samples, whereby measurement results over 3 days with 3 lots in 3 replicates will be available. When selecting a sample, it is checked whether the measuring ranges for all parameters are covered. The precision results are (statistically) pooled over the samples. The number of samples required is determined in simulations. However, a prerequisite for the (statistical) pooling of the results is a homogeneity of variance over the measuring range, ie for each parameter either the standard deviation or the CV is independent of the concentration.
VBA solution:
The data are read in, although there may be variability in the number of factors, the measurement parameters and the number of samples. An outlier detection is carried out. A graphic window allows you to "click through" quickly through the measurement results, outliers are marked. The variance components are estimated using an R program integrated in the Excel tool. The results are stored in a separate, printable and storable spreadsheet.
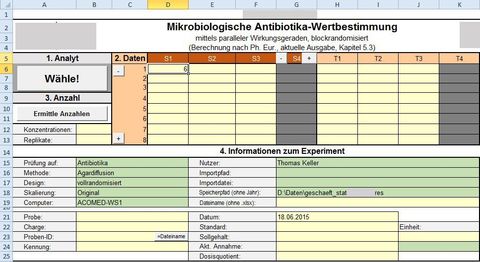
Example: Tool value determination using parallel lines of effectiveness for a pharmaceutical test laboratory, including the development of new criteria for the validity of the experiments
Task:
In an existing tool, many experiments were found to be invalid according to the procedure in accordance with the guideline (Chapter 5.3 of Ph. Eur. 7 2011) (signals from the significance tests for deviations from parallelism or from homogeneity of variances). The reasons for this had to be determined.
Methodological solution:
The significance tests were not used adequately in the guideline, it is the case that the null hypothesis should be proven, for which statistical tests are not suitable. This has also been described in the literature [Hauck Walter W., Assessing Parallelism Prior to Determining Relative Potency, PDA J. Pharmaceutical Science Technology 59: 127-137)]. E
Equivalence tests must be formulated. For parallelism, the Fieller confidence interval for the ratio of the increases was used. (In a newer version of the guideline, this procedure is now also planned - in addition to the old procedure.)
The equivalence limits must also be set. Historical data was used for this. This gave rise to the task of programming a new tool. These limits are checked annually.
VBA solution:
Creation of a tool for a series of typical experiments with different designs and different numbers of replicas. Integration of an R tool for calculating the Fieller AI. Detection of any incorrect entries. Validation through parallel programming in SAS and extensive test runs. The results are stored in a separate, printable and storable spreadsheet. These saved results can later be read in again with a separate tool to verify the historical limits.
Literature: Development of an adequate statistical procedure
for the evaluation of parallel line assays, 2014, p. 3. link